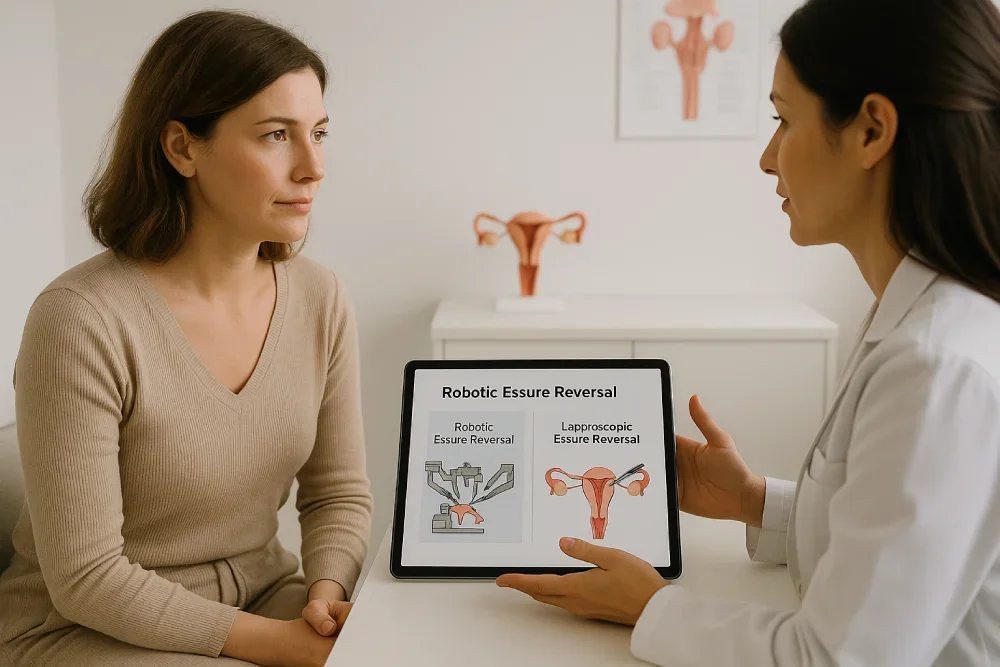
Robotic vs. Laparoscopic Essure Reversal: Which Is Better?
Categories:
By: Ethan Cole
Essure reversal is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring fertility after having the Essure device, a permanent birth control method, placed in the fallopian tubes. Many women seek this procedure due to changing reproductive goals or symptoms caused by the device. Understanding the differences between the two main minimally invasive techniques—robotic and laparoscopic approaches—is essential for making an informed decision tailored to one’s health needs and fertility goals.
Both robotic and laparoscopic Essure reversal involve precise removal of the device and reconnection of the fallopian tubes. While robotic surgery offers enhanced visualization and dexterity, laparoscopy remains widely used for its effectiveness and lower cost. This article explores the advantages, drawbacks, and patient outcomes of each method.
Key Takeaways
Robotic and laparoscopic Essure reversal both safely remove the device and restore fertility, offering minimally invasive options with low complication rates and high patient satisfaction.
Pregnancy success rates after reversal average 36%–38%, comparable to IVF, with many women also reporting improved symptoms like pelvic pain and abnormal bleeding.
Robotic surgery offers enhanced 3D visualization, wristed instruments, and lower blood loss (~10 mL), making it ideal for complex cases, but comes with higher costs.
Laparoscopic reversal is more cost-effective and widely available, with slightly longer operative time (~45 minutes) but comparable recovery and fertility outcomes.
Surgeon expertise is the most critical factor: robotic assists precision in complex reconstructions, while laparoscopy requires advanced microsurgical skill for successful outcomes.
Procedure selection should weigh fertility goals, patient anatomy, health factors, costs, and technology availability, guided by a consultation with a fertility specialist.
Understanding Essure Reversal
Essure reversal is a surgical procedure to remove the Essure device—a permanent birth control implant—and restore fallopian tube function. Women typically seek this surgery to regain fertility or relieve symptoms related to the device. Before exploring reversal options, it is important to understand what Essure is and why reversal may be necessary.
What Is Essure and Why Is Reversal Needed?
Essure is a small metal coil inserted hysteroscopically into the fallopian tubes to cause scar tissue formation, blocking the tubes and preventing pregnancy. The device was approved by the FDA in 2002, and it is estimated that hundreds of thousands of women worldwide, including over 750,000 in the U.S., have undergone Essure placement. It is highly effective, with studies reporting a 99.83% effectiveness rate at preventing pregnancy when used as directed.
However, some women experience adverse effects such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, device migration, or failure to prevent pregnancy, prompting the need for removal or reversal. According to FDA data, pain is reported in approximately 60% of device removal cases, with other reasons including device dislocation, uterine perforation, and adverse reactions. Symptoms improve or resolve in about 43%–45% of patients after device removal.
Pregnancy Success After Essure Reversal
Natural pregnancy rates after Essure reversal range from 36% to 38% within 12 months, comparable to single-cycle IVF success (around 37%).
Symptom relief after removal is reported by approximately 75% of women, with 53% seeing a reduction in pelvic pain.
Despite being permanent birth control, reversal surgery offers many women a realistic chance to conceive naturally post-procedure.
|
Metric |
Statistic & Source |
|
Total Essure procedures in U.S. |
Over 750,000 women |
|
Effectiveness rate |
99.83% pregnancy prevention with proper use |
|
Percent reporting pain |
60% of device removal reports cite pain |
|
Natural pregnancy after reversal |
36%-38% within 12 months post-surgery |
|
Symptom relief post-removal |
43%-45% report full or partial symptom resolution |
|
Pelvic pain improvement |
Approximately 53% report improvement |
Essure reversal is a technically demanding surgery but has become increasingly successful due to advancements in microsurgical techniques. Women considering this option should consult specialists to understand the potential benefits and risks based on their individual circumstances.
Surgical Approaches to Essure Reversal
Essure reversal is a technically intricate surgery that involves two main steps: the complete removal of the Essure device and the delicate reconstruction of the fallopian tubes to restore fertility. This procedure can be performed through minimally invasive techniques, primarily laparoscopic or robotic surgery. Each approach has unique features, advantages, and limitations that influence outcomes, operative times, costs, and recovery.
Laparoscopic Essure Reversal
Laparoscopic surgery for Essure reversal involves small abdominal incisions through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted. The surgeon carefully dissects and removes the Essure coils embedded in the fallopian tubes, typically performing a salpingectomy (removal of the affected tube segment). The remaining healthy tubal segments are then microsurgically reconnected or reimplanted, often requiring precise suturing under magnification.
Advantages of laparoscopy include:
Less invasive than open surgery with faster recovery and less postoperative pain
Proven safety with no major complications reported in several case series
Shorter operative time in comparison with robotic surgery in some reports (averaging around 45 minutes)
Limitations:
Two-dimensional camera view that can reduce depth perception for the surgeon
Requires high surgical skill and experience for precise tubal reconnection
May have slightly more blood loss compared to robotic approach
Robotic Essure Reversal
Robotic-assisted surgery uses a similar laparoscopic access but with robotic arms controlled by the surgeon from a console. The robot provides three-dimensional high-definition visualization, enhanced dexterity with wristed instruments, and elimination of surgeon tremors. This can be particularly advantageous when performing delicate microsurgical tubal reconnections after Essure removal.
Benefits of robotic surgery include:
Enhanced precision and control during critical surgical steps
Three-dimensional visualization enabling better tissue handling and suturing
Reduced intraoperative blood loss observed compared to laparoscopic approach (e.g., 10 mL vs 25 mL)
Drawbacks:
Higher cost of surgery due to robotic equipment and longer operating room times
Availability limited to centers with robotic surgical expertise
Slightly longer total operating time reported in some cases
Both approaches have demonstrated safety and efficacy in removing Essure devices and potentially restoring fertility. Choice between laparoscopic and robotic Essure reversal should be individualized, considering the surgeon’s expertise, available technology, patient health status, and financial factors.
Comparing Robotic and Laparoscopic Essure Reversal
When considering Essure reversal surgery, choosing between robotic and laparoscopic approaches depends on multiple factors, including precision, operative time, costs, safety, and patient outcomes.
Both methods offer minimally invasive options to remove Essure devices and restore fertility but differ in technique and resource requirements.
Precision and Visualization
Robotic surgery provides enhanced three-dimensional visualization with magnification and improved dexterity through wristed instruments. This facilitates precise dissection and suturing during fallopian tube reconstruction, minimizing tremor and surgeon fatigue. In contrast, laparoscopic surgery uses a two-dimensional camera view, requiring greater manual dexterity and experience from the surgeon.
Operative Time and Recovery
A study comparing the two techniques found robotic Essure removal averaged 30 minutes of operative time (60 minutes total in the OR) while laparoscopic surgery took about 45 minutes (65 minutes total).
Both methods resulted in low blood loss (10 mL robotic vs. 25 mL laparoscopic) and no intraoperative or postoperative complications. Recovery times were similarly favorable, with most patients symptom-free by 3 months.
Cost Considerations
Robotic surgery is generally more expensive due to costly equipment, maintenance, and longer setup time. Laparoscopy remains more cost-effective and widely available but may require higher surgical skill levels.
Safety and Complications
Both approaches have demonstrated safety without major complications. Studies report minimal blood loss, low complication rates, and effective symptom resolution post-surgery. Risks inherent to surgery, such as infection or bleeding, remain low in expert hands regardless of method.
Patient Outcomes
Patient symptom relief and successful device removal outcomes are comparable between laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Robotic surgery may offer advantages in complex cases requiring intricate suturing, yet laparoscopy achieves similar pregnancy and symptom relief rates when performed by skilled surgeons.
|
Comparison Aspect |
Robotic Essure Reversal |
Laparoscopic Essure Reversal |
|
Visualization |
3D, magnified, tremor-free |
2D, requires high skill |
|
Operative Time |
~30 minutes (60 min total OR time) |
~45 minutes (65 min total OR time) |
|
Blood Loss |
~10 mL |
~25 mL |
|
Cost |
Higher (equipment, setup, maintenance) |
Lower, more cost-effective |
|
Complications |
Very low; no major complications reported |
Very low; no major complications reported |
|
Recovery |
Similar recovery and symptom resolution |
Similar recovery and symptom resolution |
|
Patient Outcomes |
Comparable pregnancy rates and symptom relief |
Comparable pregnancy rates and symptom relief |
Which Surgical Approach Is Right for You?
Choosing between robotic and laparoscopic Essure reversal depends on several important factors, including personal fertility goals, surgeon expertise, cost considerations, and access to technology.
Factors Influencing the Choice
Fertility Goals: Women aiming for natural pregnancy and device removal may benefit from the approach best suited for precise fallopian tube repair. Both robotic and laparoscopic reversals have demonstrated pregnancy success rates around 36% to 38%, comparable to a single IVF cycle (~37%).
Surgeon Experience: The success of either approach greatly depends on the surgeon’s specialization and microsurgical skill. High expertise in tubal reconstruction is essential regardless of technique.
Cost and Accessibility: Robotic surgery typically incurs higher costs due to expensive equipment and operative time. Laparoscopy is more cost-effective and widely available but requires substantial technical skill.
Patient Health and Complexity: Robotic surgery’s enhanced visualization and dexterity may benefit complex cases requiring meticulous tubal repair. Laparoscopy is efficient for straightforward cases with favorable anatomy.
Summary Table: Factors to Consider
|
Factor |
Robotic Essure Reversal |
Laparoscopic Essure Reversal |
|
Pregnancy Success |
~36%-38% natural pregnancy rate |
~36%-38% natural pregnancy rate |
|
Surgeon Skill Needed |
Specialized robotic microsurgical skill |
Advanced laparoscopic microsurgical skill |
|
Cost |
Higher due to technology |
Lower, more affordable |
|
Availability |
Limited to centers with robotic systems |
More widely available |
|
Best for |
Complex repairs, precise suturing |
Simpler cases, cost-conscious patients |
Ultimately, discussing individual medical history, fertility plans, and surgical options with a qualified specialist is essential to tailor the approach that optimizes outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Robotic and laparoscopic Essure reversal surgeries both offer safe, minimally invasive options to remove the Essure device and restore fertility or relieve symptoms. Robotic surgery provides enhanced precision and three-dimensional visualization, potentially benefiting complex cases, but at a higher cost.
Laparoscopic surgery remains highly effective, more accessible, and cost-efficient when performed by skilled surgeons. Success rates for natural pregnancy after reversal are comparable between both methods, around 36% to 38%.
Ultimately, the best surgical approach should be tailored to individual patient goals, surgeon expertise, and resources through a thorough consultation with a fertility specialist.
Compare your Essure reversal options with Dr. Jason Neef to better understand the benefits, risks, and costs of each approach. Schedule a consultation today to discuss whether robotic or laparoscopic surgery may be right for you.
Compare your Essure reversal options with Dr. Neef today.
Call (817) 568-8731Categories:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Pregnancy rates after Essure reversal range between 40%-60%, aiming to restore fertility, whereas removal primarily relieves symptoms without restoring fertility.
-
Robotic Essure removal averages 30 minutes operative time, shorter than the laparoscopic average of 45 minutes, though total operating room time may be similar.
-
Robotic surgery’s enhanced precision and three-dimensional visualization enable meticulous device extraction, lowering risk of fragmentation compared to laparoscopy’s two-dimensional view.
-
Both robotic and laparoscopic methods show very low complication rates and comparable recovery times, with most patients symptom-free by three months post-surgery.
-
Robotic procedures tend to be costlier due to equipment and setup, with variable insurance coverage; laparoscopic surgery is generally less expensive and more widely covered.
-
Symptoms like pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, and device-related discomfort improve in about 43%-75% of women following removal.
-
High surgical skill is required for success; robotic surgery may benefit complex cases, while laparoscopy demands advanced laparoscopic microsurgical expertise.
-
Many patients achieve natural pregnancy post-reversal, with chances comparable to a single IVF cycle (~37%), and some achieving multiple pregnancies.
-
Risks include infection, bleeding, and tubal damage; tubal reconnection quality critically affects pregnancy potential and ectopic pregnancy risk.
-
Patients with complex anatomy or health issues may benefit from robotic enhancement; healthier, uncomplicated cases may be suited for laparoscopy.