Robotic Essure Reversal Pregnancy Success by Age Group
Categories:
By: Ethan Cole
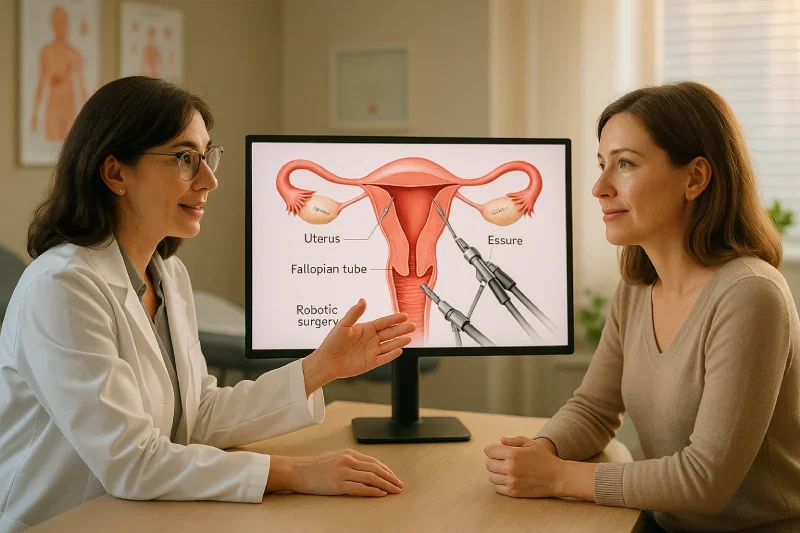
Robotic Essure reversal is a complex surgical procedure that involves removing the Essure sterilization device and attempting to restore fertility through fallopian tube reconnection. This minimally invasive approach uses advanced robotic technology to perform delicate microsurgical work with enhanced precision.
Understanding what to expect from this procedure is crucial because Essure reversal remains an experimental treatment with uncertain outcomes. While some women achieve pregnancy success rates between 40-60%, the extensive scarring and damage caused by Essure devices makes fertility restoration challenging and unpredictable.
The robotic approach primarily focuses on safe device removal to alleviate symptoms caused by Essure complications. While fertility restoration is attempted during the procedure, many patients may require additional reproductive interventions like IVF to achieve pregnancy. Setting realistic expectations about both the surgical process and potential outcomes helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Key Takeaways
Robotic Essure reversal is an experimental procedure combining device removal with fertility restoration attempts, achieving 40-60% pregnancy rates in limited studies.
Surgery involves complex device extraction and tubal reconnection phases, requiring 2-4 hours of operating time with advanced robotic microsurgical techniques for precision.
Recovery typically takes 2-3 weeks with faster healing than traditional surgery, though anesthesia effects may extend the recovery timeline for some patients.
Most patients experience symptom relief from device removal, but fertility restoration remains uncertain due to extensive Essure-related scarring and tissue damage.
Alternative treatments like IVF often provide more predictable fertility outcomes than experimental reversal surgery, especially for women over 35 years old.
Success depends on individual factors including age, extent of tubal damage, and surgical expertise, with many patients requiring additional fertility interventions regardless.
Pre-Procedure Preparation and Evaluation
Comprehensive evaluation before robotic Essure reversal ensures patients understand the experimental nature of the procedure and helps surgeons assess individual candidacy. This preparation phase sets realistic expectations about potential outcomes and alternative treatment options.
Medical Assessment and Testing
Fertility Evaluation:
Comprehensive hormone testing to assess ovarian function and reserve
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) to evaluate current tubal status and Essure device position
Pelvic ultrasound to assess reproductive organ health and identify complications
Partner fertility testing including semen analysis and hormone evaluation
Complete blood work including infection screening and clotting studies
Overall Health Assessment:
Physical examination focusing on reproductive and cardiovascular health
Review of current symptoms potentially related to Essure devices
Assessment of previous pregnancies, surgeries, and medical conditions
Evaluation of medications that might affect surgery or fertility
Psychological readiness assessment for experimental procedure with uncertain outcomes
Surgical Consultation Process
Detailed Discussion Topics:
Experimental nature of Essure reversal and limited long-term data
Individual success rate predictions based on age and health factors
Alternative treatment options including IVF and device removal without reversal
Realistic timeline for recovery and potential fertility restoration
Financial considerations including insurance coverage limitations
Informed Consent Requirements:
Understanding that fertility restoration is not guaranteed
Acknowledgment of potential need for additional fertility treatments
Recognition of surgical risks and possible complications
Agreement to follow post-operative monitoring and care protocols
Realistic expectations about symptom relief versus fertility outcomes
Understanding Risks and Limitations
|
Risk Category |
Specific Concerns |
Likelihood |
Impact |
|
Surgical Risks |
Bleeding, infection, organ damage |
Low with robotic technique |
Immediate complications |
|
Fertility Risks |
Failed tube reconnection, ectopic pregnancy |
Moderate to high |
Long-term reproductive impact |
|
Experimental Nature |
Uncertain long-term outcomes, limited data |
High |
Unknown future implications |
|
Recovery Complications |
Extended healing, anesthesia effects |
Low to moderate |
Short-term quality of life |
|
Need for Additional Treatment |
IVF requirement, repeat surgeries |
Moderate to high |
Financial and emotional burden |
Key Limitations to Understand:
Essure-related scarring may prevent successful tubal reconnection
Pregnancy rates remain uncertain due to limited long-term studies
Many patients require IVF even after successful device removal
Symptom relief does not guarantee fertility restoration
Recovery may take longer than anticipated due to individual healing factors
The Robotic Surgery Process: Step-by-Step
The robotic Essure reversal procedure involves multiple complex phases requiring advanced surgical skill and specialized robotic equipment. Understanding each step helps patients prepare for the surgical experience and recovery process.
Device Extraction Phase
The surgery begins with careful positioning of the patient under general anesthesia, followed by creation of multiple small incisions to accommodate robotic instruments. Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity to create working space and enhance visualization of internal structures.
The robotic camera system provides surgeons with 3D magnified views of the reproductive organs, allowing precise identification of Essure device locations within the fallopian tubes. This enhanced visualization is crucial because the devices may be embedded in scar tissue or positioned differently than originally placed.
Surgeons systematically examine each fallopian tube to locate all Essure components, including the metal coils and surrounding fibrous material. The extraction process requires careful dissection around the devices to avoid damaging any remaining healthy tubal tissue that might be suitable for reconnection attempts.
Tubal Assessment and Reconnection Attempts
Once the Essure devices are completely removed, surgeons evaluate the condition of remaining tubal tissue through microscopic examination. This assessment determines whether fertility restoration attempts are feasible or if the damage is too extensive for successful reconnection.
Key Assessment Factors:
Length of remaining healthy fallopian tube segments
Quality of blood supply to remaining tissue
Extent of scarring and inflammatory damage
Condition of uterine cornua for potential reimplantation
Overall structural integrity of reproductive anatomy
The reconnection process involves resecting damaged portions of the uterine cornua where Essure devices caused scarring, then carefully reimplanting healthy tubal segments using precise microsurgical techniques. This delicate work requires suturing tissue layers while maintaining proper alignment and blood flow.
Minimally Invasive Robotic Techniques
Robotic technology transforms this complex microsurgical procedure by providing enhanced dexterity and precision that surpasses human hand capabilities. The robotic instruments eliminate natural tremor and allow for scaled movements, where large hand motions translate into precise, controlled instrument movements.
The three-dimensional magnified visualization helps surgeons distinguish between healthy and damaged tissue more accurately than traditional laparoscopic methods. This improved visualization becomes particularly important when working around extensive scar tissue caused by Essure devices.
Multiple robotic instruments can work simultaneously under direct surgeon control, improving surgical efficiency and reducing operative time. The enhanced ergonomics reduce surgeon fatigue during these lengthy, complex procedures, maintaining precision throughout the entire operation.
What Happens During Surgery
The surgical experience for robotic Essure reversal typically takes 2-4 hours depending on the complexity of device removal and the extent of reconnection attempts. Patients remain under careful medical supervision throughout the entire procedure to ensure safety and optimal outcomes.
Anesthesia and Patient Monitoring
General anesthesia is administered to ensure complete comfort and immobility during the delicate microsurgical work. The anesthesia team monitors vital signs continuously, including heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and breathing patterns throughout the procedure.
Advanced monitoring equipment tracks multiple physiological parameters simultaneously, allowing immediate response to any changes in patient condition. Temperature regulation systems maintain optimal body temperature, while fluid management ensures proper hydration and blood pressure stability.
The anesthesia effects may extend recovery time beyond the typical 2-3 week healing period, particularly for patients sensitive to anesthetic medications. Most patients experience grogginess for several hours after surgery, with complete anesthesia recovery occurring within 24-48 hours.
Surgical Timeline and Duration
|
Surgery Phase |
Duration |
Activities |
Patient Status |
|
Pre-operative Setup |
30-45 minutes |
Anesthesia, positioning, robotic system preparation |
Unconscious, stable monitoring |
|
Device Extraction |
60-90 minutes |
Locating and removing Essure components |
Continuous vital sign monitoring |
|
Tissue Assessment |
30-60 minutes |
Evaluating remaining tubal tissue quality |
Stable anesthesia maintenance |
|
Reconnection Attempts |
60-120 minutes |
Microsurgical tubal reimplantation |
Enhanced monitoring during complex phase |
|
Closure and Recovery |
30-45 minutes |
Closing incisions, reversing anesthesia |
Transition to recovery monitoring |
Transition to recovery monitoring
The total surgical time varies significantly based on the extent of Essure-related damage and the complexity of reconnection attempts. Cases with extensive scarring or multiple device fragments may require additional time for safe and complete removal.
Real-Time Surgical Decisions
Surgeons must make critical decisions throughout the procedure based on their findings during tissue examination. The experimental nature of Essure reversal means that each case presents unique challenges requiring adaptive surgical approaches.
When extensive scarring is encountered, surgeons may decide to focus primarily on device removal rather than attempting fertility restoration. This decision protects patients from additional surgical trauma while still providing symptom relief from Essure-related complications.
The condition of remaining tubal tissue often determines whether reconnection attempts are worthwhile or if patients should be counseled toward IVF for future fertility goals. Surgeons may discover during surgery that the damage is too extensive for meaningful fertility restoration, leading to modified surgical objectives.
Communication with the surgical team continues throughout the procedure, with decisions documented for post-operative discussions with patients about realistic expectations for fertility outcomes and potential need for additional reproductive interventions.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Recovery from robotic Essure reversal is generally faster than traditional open surgery due to the minimally invasive approach, but patients should expect a significant healing period of 2-3 weeks. The complexity of the procedure and individual responses to anesthesia can extend recovery time beyond initial expectations.
Immediate Post-Surgery (Days 1-3)
The first 24-48 hours after surgery focus on managing anesthesia effects and monitoring for immediate complications. Patients typically experience grogginess, nausea, and disorientation as anesthetic medications wear off. Pain levels are generally moderate and manageable with prescribed medications.
Most patients can go home the same day or after an overnight observation period, depending on their response to anesthesia and overall condition. Initial discomfort comes primarily from the carbon dioxide gas used during surgery, which can cause shoulder pain as the gas is absorbed by the body.
Walking is encouraged within hours of surgery to prevent blood clots and promote healing, but patients should avoid any strenuous activity. Light meals can usually be tolerated once nausea subsides, typically within 12-24 hours post-surgery.
Early Recovery Phase (Weeks 1-2)
Activity Restrictions and Guidelines:
No lifting objects heavier than 10 pounds
Driving prohibited while taking prescription pain medications
Return to desk work typically possible within 5-7 days
Light household activities allowed with frequent rest periods
Showering permitted but avoid soaking in baths or swimming pools
Expected Recovery Milestones:
Incision sites begin healing with minimal scarring
Energy levels gradually improve but fatigue remains common
Pain transitions from moderate to mild discomfort
Sleep patterns normalize as medication needs decrease
Follow-up appointments scheduled to monitor healing progress
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention:
Fever above 101°F or signs of infection
Heavy bleeding or unusual discharge
Severe abdominal pain not controlled by medication
Difficulty urinating or persistent nausea and vomiting
Increasing pain rather than gradual improvement
Complete Recovery (Weeks 2-3)
Full recovery typically occurs within 2-3 weeks, though some patients may require additional time depending on their individual healing response and any complications encountered during surgery. Normal activities can gradually resume, including exercise and unrestricted daily tasks.
Sexual activity is usually cleared after the follow-up appointment confirms proper healing of internal tissues. However, patients should understand that fertility restoration may not be immediate even after complete surgical recovery.
The timeline for attempting pregnancy varies based on surgical findings and healing progress. Some patients may be cleared to try conceiving within 2-3 months, while others may need additional time for optimal tissue healing. Many patients discover during follow-up testing that fertility has not been restored despite successful device removal, requiring consideration of IVF or other reproductive interventions.
Recovery marks the beginning of the evaluation period to determine whether the experimental procedure achieved its fertility restoration goals, setting the stage for important decisions about future reproductive treatment options.
Realistic Outcomes and Success Rates
Setting realistic expectations about robotic Essure reversal outcomes is crucial because this procedure remains experimental with limited long-term data. While some women achieve pregnancy, the extensive damage caused by Essure devices makes fertility restoration unpredictable and often unsuccessful.
40-60% Pregnancy Success Range
The reported pregnancy success rates for Essure reversal vary widely due to limited studies and different patient populations. This broad range reflects the experimental nature of the procedure and the significant challenges posed by Essure-related tissue damage.
Success rates depend heavily on the extent of scarring and inflammation caused by the original Essure devices. Some women experienced minimal tissue damage and may have better reconnection potential, while others developed extensive fibrosis that makes fertility restoration nearly impossible.
The 40-60% range also reflects differences in surgical expertise and patient selection criteria. Centers with more experience may achieve better outcomes by carefully selecting candidates with the best potential for success, while the lower end of the range may represent outcomes from less experienced surgical teams or more challenging cases.
Patient age significantly influences these success rates, with younger women having better outcomes than those over 35. However, even optimal candidates face uncertainty about long-term fertility restoration due to the experimental nature of the procedure.
Experimental Nature of the Procedure
Limited Scientific Evidence:
Few long-term studies available on fertility outcomes after Essure reversal
No standardized surgical techniques or protocols established across medical centers
Uncertain data on tube function and pregnancy success over multiple years
Limited understanding of factors that predict successful versus failed outcomes
Insufficient research on optimal patient selection criteria for best results
Unknown Long-term Implications:
Uncertainty about ectopic pregnancy risks with reconnected tubes
Unknown effects on future pregnancy complications or delivery outcomes
Lack of data on repeat pregnancy success rates after initial conception
Unclear timeline for fertility restoration even in successful cases
Limited information about long-term tube function and patency maintenance
Medical Community Caution:
Most fertility specialists recommend IVF over reversal for Essure patients
Professional medical organizations have not established treatment guidelines
Many insurance companies do not cover experimental fertility procedures
Ongoing research needed to establish safety and efficacy standards
Patient counseling emphasizes experimental nature and uncertain outcomes
Symptom Relief vs. Fertility Restoration
|
Outcome Type |
Success Rate |
Timeline |
Patient Impact |
|
Device Removal |
95%+ |
Immediate |
Eliminates foreign body complications |
|
Symptom Relief |
70-85% |
2-6 months |
Reduces pain, bleeding, allergic reactions |
|
Tubal Patency |
60-75% |
3-6 months |
Open tubes but not necessarily functional |
|
Pregnancy Achievement |
40-60% |
6-18 months |
Actual fertility restoration success |
|
Live Birth Outcome |
30-45% |
9-18 months |
Complete reproductive success |
Complete reproductive success
Many patients experience significant symptom relief from device removal even when fertility is not restored. Chronic pelvic pain, irregular bleeding, and allergic reactions often improve substantially after successful Essure removal, providing quality of life benefits regardless of pregnancy outcomes.
The distinction between open tubes and functional fertility is important for patient understanding. Testing may show that tubes are open following surgery, but this does not guarantee that they can support natural conception or maintain pregnancy successfully.
Most medical experts emphasize that symptom relief should be the primary goal of Essure removal surgery, with fertility restoration considered a potential but uncertain secondary benefit that may require additional reproductive interventions to achieve.
Risks and Complications to Consider
While robotic Essure reversal offers potential benefits, patients must understand the significant risks associated with this experimental procedure. The complexity of removing embedded devices and attempting fertility restoration creates both immediate surgical risks and long-term uncertainties.
Surgical Risks During Procedure
Immediate surgical complications can occur during robotic Essure reversal due to the complex nature of device removal and tissue reconstruction. Bleeding represents a primary concern, particularly when Essure devices have become embedded in vascular areas or when extensive dissection is required to remove all device components.
Infection risks exist with any surgical procedure, though robotic techniques generally reduce this risk compared to open surgery. However, the experimental nature of Essure reversal means that optimal antibiotic protocols and infection prevention strategies are not well established.
Damage to surrounding organs poses another significant risk during device removal. The fallopian tubes lie close to important structures including the ovaries, uterus, bladder, and bowel. Extensive scarring around Essure devices can make tissue planes difficult to identify, increasing the risk of inadvertent organ injury.
Anesthesia complications may be more likely in patients who have experienced chronic health issues related to their Essure devices. Some women report autoimmune-like symptoms that could affect their response to anesthesia and surgical stress.
Long-term Complications
Reproductive System Risks:
Ectopic pregnancy rates may be higher than normal due to altered tubal anatomy
Uterine rupture risk during future pregnancies from cornual reconstruction
Chronic pelvic pain may persist or worsen despite device removal
Ovarian function may be affected by surgical trauma or adhesion formation
Future fertility treatments may be more complicated due to surgical scarring
Uncertain Outcomes:
Long-term tube function remains unpredictable even after successful surgery
Adhesion formation may block tubes or cause pain months or years later
Unknown effects on hormone levels and menstrual cycle regularity
Potential need for repeat surgeries if complications develop
Unclear timeline for determining whether fertility has been restored
Quality of Life Impacts:
Recovery may be longer and more difficult than anticipated
Emotional stress from uncertain outcomes and experimental nature
Financial burden from procedure costs and potential additional treatments
Relationship strain from fertility uncertainties and treatment decisions
Ongoing medical monitoring requirements for indefinite periods
When Additional Interventions May Be Needed
Many patients require additional reproductive interventions even after technically successful Essure reversal surgery. IVF becomes necessary when tubes remain blocked, function poorly, or when other fertility factors prevent natural conception.
The decision to pursue IVF often comes several months after reversal surgery when it becomes clear that natural conception is not occurring. This delay can be emotionally and financially challenging for couples who hoped the reversal would restore normal fertility.
Some patients may need repeat surgeries to address complications like adhesion formation or incomplete device removal discovered during follow-up testing. These additional procedures carry their own risks and may further compromise reproductive function.
Counseling and psychological support often become necessary as couples navigate the uncertainty of experimental treatment outcomes. The stress of uncertain fertility restoration can strain relationships and require professional intervention to manage effectively.
Alternative reproductive technologies like egg freezing may be recommended for younger patients while they attempt natural conception after reversal, providing backup options if the experimental procedure fails to restore fertility as hoped.
Risks and Complications to Consider
While robotic Essure reversal offers potential benefits, patients must understand the significant risks associated with this experimental procedure. The complexity of removing embedded devices and attempting fertility restoration creates both immediate surgical risks and long-term uncertainties.
Surgical Risks During Procedure
Immediate surgical complications can occur during robotic Essure reversal due to the complex nature of device removal and tissue reconstruction. Bleeding represents a primary concern, particularly when Essure devices have become embedded in vascular areas or when extensive dissection is required to remove all device components.
Infection risks exist with any surgical procedure, though robotic techniques generally reduce this risk compared to open surgery. However, the experimental nature of Essure reversal means that optimal antibiotic protocols and infection prevention strategies are not well established.
Damage to surrounding organs poses another significant risk during device removal. The fallopian tubes lie close to important structures including the ovaries, uterus, bladder, and bowel. Extensive scarring around Essure devices can make tissue planes difficult to identify, increasing the risk of inadvertent organ injury.
Anesthesia complications may be more likely in patients who have experienced chronic health issues related to their Essure devices. Some women report autoimmune-like symptoms that could affect their response to anesthesia and surgical stress.
Long-term Complications
Reproductive System Risks:
Ectopic pregnancy rates may be higher than normal due to altered tubal anatomy
Uterine rupture risk during future pregnancies from cornual reconstruction
Chronic pelvic pain may persist or worsen despite device removal
Ovarian function may be affected by surgical trauma or adhesion formation
Future fertility treatments may be more complicated due to surgical scarring
Uncertain Outcomes:
Long-term tube function remains unpredictable even after successful surgery
Adhesion formation may block tubes or cause pain months or years later
Unknown effects on hormone levels and menstrual cycle regularity
Potential need for repeat surgeries if complications develop
Unclear timeline for determining whether fertility has been restored
Quality of Life Impacts:
Recovery may be longer and more difficult than anticipated
Emotional stress from uncertain outcomes and experimental nature
Financial burden from procedure costs and potential additional treatments
Relationship strain from fertility uncertainties and treatment decisions
Ongoing medical monitoring requirements for indefinite periods
When Additional Interventions May Be Needed
Many patients require additional reproductive interventions even after technically successful Essure reversal surgery. IVF becomes necessary when tubes remain blocked, function poorly, or when other fertility factors prevent natural conception.
The decision to pursue IVF often comes several months after reversal surgery when it becomes clear that natural conception is not occurring. This delay can be emotionally and financially challenging for couples who hoped the reversal would restore normal fertility.
Some patients may need repeat surgeries to address complications like adhesion formation or incomplete device removal discovered during follow-up testing. These additional procedures carry their own risks and may further compromise reproductive function.
Counseling and psychological support often become necessary as couples navigate the uncertainty of experimental treatment outcomes. The stress of uncertain fertility restoration can strain relationships and require professional intervention to manage effectively.
Alternative reproductive technologies like egg freezing may be recommended for younger patients while they attempt natural conception after reversal, providing backup options if the experimental procedure fails to restore fertility as hoped.
Conclusion
Robotic Essure reversal is an experimental procedure that combines device removal with fertility restoration attempts, achieving pregnancy rates of 40-60% in limited studies. While robotic technology reduces surgical trauma and speeds recovery to 2-3 weeks, the extensive damage caused by Essure devices makes successful fertility restoration uncertain and unpredictable. Most patients experience symptom relief from device removal, but many require additional interventions like IVF to achieve pregnancy. Understanding the experimental nature, realistic success rates, and alternative treatment options helps patients make informed decisions about this complex procedure with uncertain long-term outcomes.
Ready to explore robotic Essure reversal options? Dr. Jason Neef provides comprehensive evaluation and realistic guidance about experimental fertility restoration procedures.
Contact Dr. Jason Neef for expert consultation on Essure removal and fertility restoration alternatives.
Schedule your robotic Essure procedure consultation with Dr. Neef today.
Call (817) 568-8731Categories:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
The procedure involves making 3-4 small incisions to access the fallopian tubes using robotic arms. The Essure coils are carefully removed. The surgeon then reconnects the fallopian tubes surgically, often reimplanting the tube into the uterus with microsurgical precision. The procedure takes about 30-45 minutes and is outpatient.
-
Robotic Essure removal focuses mainly on removing the device and scar tissue to relieve symptoms, with a quicker recovery and symptom relief. Reversal aims to restore fertility by reconnecting tubes, which is more complex and has uncertain fertility success, but benefits from robotic precision and minimally invasive methods.
-
Essure causes extensive scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, making it difficult to restore normal tubal function fully. Limited data exist on pregnancy outcomes post-reversal, with some success but also risks like ectopic pregnancy. The procedure remains experimental with no guaranteed fertility restoration.
-
Initial recovery includes mild pain and tenderness around incision sites for a few days. Patients often resume normal activities within 1-2 weeks. Full healing typically occurs over 2-3 weeks. Most report less pain and quicker recovery compared to traditional surgery due to the minimally invasive robotic approach.
-
Robotic reversal offers the potential to restore fertility by reconnecting fallopian tubes. However, the success rate varies, with some women achieving pregnancy but others facing infertility due to tubal damage. Follow-up imaging may confirm tubal patency, but fertility is not guaranteed and may require further intervention.
-
Possible complications include bleeding, infection, anesthesia risks, damage to reproductive organs, and scarring. There is also a risk of ectopic pregnancy if the tubes do not function properly after reversal. Robotic surgery lowers risks due to precision but complications are still possible.
-
Robotic surgery offers enhanced 3D visualization, greater precision, and better dexterity with wristed instruments, allowing delicate reconstruction of fallopian tubes. It minimizes incision size, reduces tissue trauma, and shortens recovery time compared to open or conventional laparoscopy.
-
Patients undergo imaging and health evaluation, avoid food and drink after 10 pm before surgery, and receive anesthesia consultation. Preoperative instructions ensure patient safety and optimize surgical outcomes. Emotional and fertility counseling is also recommended due to variable success rates.
-
The surgery typically lasts 30 to 45 minutes for device removal and about 2 hours for full reversal with tubal reimplantation and microsurgical repair, depending on complexity. It is usually outpatient, allowing same-day discharge.
-
Removal can alleviate pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, allergic reactions, and other systemic symptoms related to Essure coils. Symptom improvement varies per individual, but many patients report relief after device removal even if fertility restoration is uncertain.