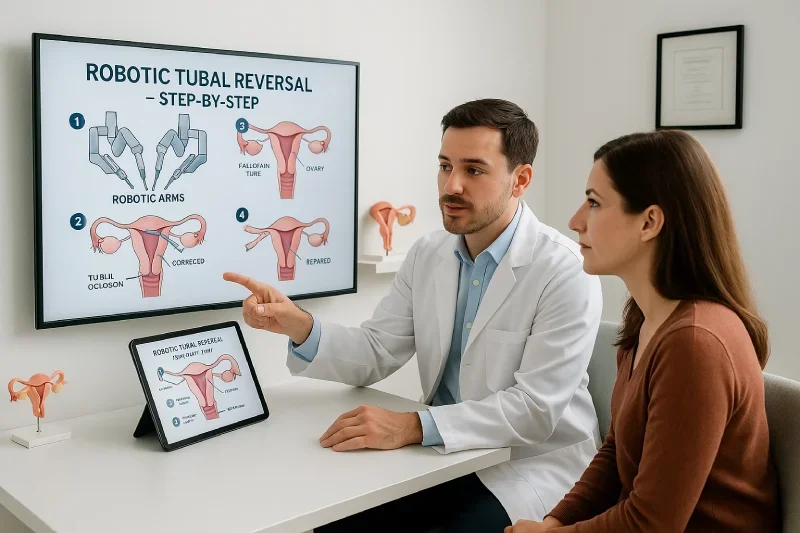
Robotic Tubal Reversal: How the Procedure Works
Categories:
By: Ethan Cole
Tubal ligation, commonly referred to as “getting your tubes tied,” is a form of permanent birth control that involves sealing or cutting the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. While the procedure is intended to be irreversible, many women later choose to restore their fertility due to changes in life circumstances or a renewed desire to conceive naturally.
Robotic tubal reversal is an advanced surgical technique that offers a minimally invasive solution for reconnecting the fallopian tubes. This method uses robotic technology to assist the surgeon in performing delicate microsurgical repairs with exceptional precision and control.
In this guide, we will explain how robotic tubal reversal works, what makes it different from traditional approaches, and why it’s becoming a preferred option for women seeking to restore their fertility. You'll also learn about the surgical steps, benefits, recovery expectations, and how to determine if you're a good candidate for the procedure.
Key Takeaways
Robotic tubal reversal is a minimally invasive procedure that reconnects fallopian tubes using robotic technology for enhanced precision, 3D visualization, and improved fertility outcomes.
Women consider reversal for reasons such as desire for more children, religious preferences, financial alternatives to IVF, or previous dissatisfaction with assisted reproduction.
Eligibility depends on factors like remaining tubal length (≥4 cm), type of original ligation, age under 43, and overall reproductive health with minimal adhesions.
The procedure involves microsurgical suturing of the tubes under 3D imaging, followed by patency testing to confirm successful reconnection and function.
Recovery is faster than traditional open surgery—most patients resume daily activities within 1–2 weeks, with full recovery in about 3–4 weeks.
Pregnancy success rates reach 60%–80%, especially in women under 38 with healthy tubes, making it a strong alternative to IVF for many patients.
What Is Robotic Tubal Reversal?
Robotic tubal reversal is a surgical procedure designed to restore fertility in women who have previously undergone tubal ligation. Using a computer-assisted robotic system, the surgeon reconnects the fallopian tubes to allow natural conception. This approach offers enhanced precision and control, particularly in cases requiring delicate microsurgical repair.
Why Women Consider Tubal Reversal
Many women who once chose permanent birth control later wish to conceive due to changes in life circumstances. Robotic tubal reversal offers a way to pursue pregnancy without relying on in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Common reasons for seeking tubal reversal include:
Desire for additional children after remarriage or a change in family plans
Personal or religious preferences for natural conception
Unsuccessful or undesirable experiences with IVF
Financial preference for a one-time surgery over multiple IVF cycles
How Robotic Tubal Reversal Differs from Traditional Methods
Unlike traditional tubal reversal performed with manual laparoscopic instruments or open surgery, robotic tubal reversal uses a robotic-assisted system controlled by the surgeon from a console. The system includes high-definition 3D imaging and wristed instruments that mimic the movements of the human hand with greater flexibility and precision.
This technology allows for more accurate suturing and less trauma to surrounding tissue, which can contribute to better outcomes and faster recovery for the patient.
Who Is a Candidate for This Procedure?
Not every woman is a candidate for robotic tubal reversal. Eligibility depends on overall reproductive health and the specifics of the original tubal ligation.
You may be a candidate if:
Your tubes were tied using clips, rings, or minimal tissue removal
You have at least 4 cm of remaining healthy fallopian tube
You are in good overall health and under the age of 43
You do not have severe pelvic adhesions or endometriosis
You wish to conceive naturally and avoid IVF
How Robotic Technology Enhances Tubal Reversal
Robotic technology plays a critical role in the precision and success of modern tubal reversal surgery. By combining high-definition imaging with micro-scale surgical tools, the robotic system enhances the surgeon’s ability to perform delicate procedures within the limited space of the pelvic cavity. This technology is especially valuable in fertility-preserving operations where accuracy is essential.
The Robotic Surgical System Explained
The robotic surgical system used in tubal reversal typically includes three main components: a surgeon console, robotic arms equipped with specialized instruments, and a high-definition 3D camera system. The robotic arms are inserted into the abdomen through small incisions, and the surgeon operates from the console, which is positioned just a few feet away.
The camera provides a magnified, three-dimensional view of the operative field, allowing the surgeon to see fine anatomical details in real time. Each robotic arm holds an instrument that mimics the movement of the surgeon’s hands but with greater stability and precision.
The Surgeon’s Role During Robotic Surgery
While the system includes advanced robotic technology, it is important to understand that the robot does not act independently. The surgeon maintains full control over every movement, directing the instruments with foot pedals and hand controls at the console.
The robotic system enhances the surgeon’s capabilities, but all decisions and actions are performed in real time by the operating physician. This method combines human judgment with machine-enhanced dexterity, offering both safety and precision.
Benefits of 3D Imaging and Wristed Instrument Control
Robotic-assisted surgery provides several advantages over traditional laparoscopic techniques:
High-definition 3D visualization of the surgical field
Greater range of motion with wristed instruments that mimic natural hand movements
Improved precision during microsurgical suturing of the fallopian tubes
Reduced surgeon fatigue due to ergonomic console design
Enhanced stability of instruments, minimizing tremor and unintentional movement
These features help improve outcomes in tubal reversal procedures where tissue preservation and accurate reconnection are essential.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Procedure
Understanding each stage of the robotic tubal reversal procedure can help patients feel more confident and prepared. The surgery involves several carefully controlled steps that prioritize tissue preservation, precision, and optimal conditions for natural fertility restoration.
Preoperative Preparation and Anesthesia
Before the surgery, patients undergo a standard preoperative evaluation to assess their overall health and eligibility. This may include lab work, imaging, and a consultation to review prior tubal ligation records. On the day of the procedure, patients are advised to fast and avoid certain medications as directed.
General anesthesia is administered to ensure comfort and immobility throughout the procedure. Once the patient is fully sedated, they are positioned for optimal access to the pelvic region.
Surgical Access and Robotic Arm Insertion
The surgeon begins by making several small incisions in the abdomen, typically less than one centimeter each. Through these incisions, trocar ports are placed to allow access for the robotic instruments and camera system.
Once the trocars are in place, the robotic arms and camera are docked. The surgeon, seated at the nearby console, begins to control the instruments remotely while viewing the internal anatomy in high-definition 3D.
Reconnecting the Fallopian Tubes With Microsurgical Suturing
The blocked or cut ends of the fallopian tubes are carefully located and evaluated. Using wristed robotic instruments, the surgeon precisely aligns the tubal segments and begins suturing them back together under magnification.
Ultra-fine sutures—sometimes thinner than a human hair—are used to minimize tissue trauma and preserve function. In some cases, a temporary stent is placed inside the tube to maintain patency during healing.
Tubal Patency Testing and Surgical Closure
Before completing the procedure, the surgeon performs a tubal patency test, often using a small amount of dye (chromopertubation) to confirm that the reconnected tubes are open and functional.
Once tubal function is confirmed, the robotic instruments are withdrawn, and the incisions are closed using dissolvable sutures. The patient is then moved to recovery for postoperative monitoring.
Benefits of Robotic Tubal Reversal
Robotic tubal reversal has become a preferred surgical approach for women seeking fertility restoration after tubal ligation. Its precision, lower trauma, and faster recovery make it a compelling option, especially for patients seeking natural conception without in vitro fertilization (IVF). While traditional reversal methods are still effective in many cases, robotic-assisted techniques offer distinct clinical and patient-centered advantages.
Why Choose Robotic Tubal Reversal?
The following table compares key aspects of robotic versus traditional tubal reversal surgery:
|
Feature |
Robotic Tubal Reversal |
Traditional (Laparoscopic/Open) Tubal Reversal |
|
Surgical Precision |
High, with micro-scale suturing |
Moderate to high, depends on surgeon skill |
|
Visualization |
3D magnified imaging |
2D video or direct visual (open) |
|
Incision Size |
Small (5–10 mm) |
Small (laparoscopy) or large (open surgery) |
|
Recovery Time |
1–2 weeks |
2–4 weeks (lap) / 4–6 weeks (open) |
|
Risk of Adhesions |
Lower due to minimal trauma |
Higher with open techniques |
|
Fertility Outcomes |
High in well-selected candidates |
Variable based on approach and case factors |
Enhanced Precision and Better Surgical Outcomes
Robotic-assisted systems allow the surgeon to operate with unmatched dexterity and stability. The ability to use wristed instruments and ultra-fine sutures under 3D magnification improves alignment of the fallopian tubes and reduces damage to surrounding tissues. This level of control contributes to more consistent results, especially in complex cases.
Faster Recovery and Lower Complication Risk
Minimally invasive access and careful handling of tissues lead to quicker recovery, less discomfort, and fewer post-surgical complications. Patients often report returning to normal activity within one to two weeks, with lower rates of pain, infection, or internal scarring compared to open surgery.
Fertility Outcomes and Success Potential
In experienced hands, robotic tubal reversal offers excellent pregnancy success rates—often 60% to 80% within the first year post-surgery for patients under 40. These outcomes are comparable or superior to other surgical methods, especially when precision and preservation of tubal function are essential.
Robotic vs Traditional Tubal Reversal
Choosing between robotic and traditional tubal reversal methods involves evaluating multiple factors—technique, recovery, success likelihood, and cost. Understanding how these approaches differ can help patients make a more informed, personalized decision.
Surgical Technique and Visualization
One of the most noticeable differences lies in how each procedure is performed. Robotic surgery uses a computer-assisted system that enhances the surgeon’s movements and provides a highly magnified 3D view. Traditional tubal reversal is performed manually, either through laparoscopy or open abdominal surgery.
|
Attribute |
Robotic Tubal Reversal |
Traditional Tubal Reversal |
|
Surgical Access |
Small incisions with robotic ports |
Small incisions (lap) or larger open cut |
|
Visualization |
3D high-definition imaging |
2D camera (lap) or direct view (open) |
|
Instrument Control |
Wristed robotic arms |
Manual instruments |
|
Suturing Precision |
Micro-scale with enhanced control |
Varies with surgeon experience |
This enhanced technology may translate into more delicate tissue handling and better outcomes in complex cases.
Recovery Time and Postoperative Experience
Robotic surgery is minimally invasive and generally results in a quicker, smoother recovery. Traditional open surgeries involve more tissue disruption, longer healing, and increased postoperative discomfort.
Recovery experience differences:
Robotic: 1–2 weeks for most daily activities
Laparoscopic: 2–3 weeks recovery
Open surgery: Up to 6 weeks for full recovery
Pain: Often less with robotic approach due to reduced trauma
Scar visibility: Smaller and less noticeable with robotic or laparoscopic access
Success Rates and Long-Term Outcomes
Success rates for both approaches depend on several factors: the patient’s age, tubal length, type of ligation, and surgeon experience.
Robotic surgery: Success rates often range from 60% to 80% in well-selected candidates
Traditional (laparoscopic or open): Similar ranges, though may be slightly lower in complex cases or open procedures
With experienced hands, both methods can achieve high fertility restoration outcomes, but robotic precision may provide an advantage in anatomically challenging cases.
Cost and Accessibility
Robotic surgery typically involves higher upfront costs due to the use of advanced equipment and longer operating room times. Traditional laparoscopic reversal is more widely available and often less expensive.
Robotic: $8,000–$12,000 on average
Laparoscopic: $5,000–$9,000
Open: Varies widely; often less common today
Insurance rarely covers either method, making cost a major deciding factor. Robotic surgery may be worth the premium in select cases, especially for patients with anatomical challenges or higher success potential.
Recovery and What to Expect After Surgery
Understanding the recovery process helps patients prepare both physically and emotionally for what comes after robotic tubal reversal. While recovery times vary slightly by individual, most patients experience a relatively smooth postoperative period due to the minimally invasive nature of the procedure.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
Immediately after surgery, patients are monitored in a recovery area until they wake fully from anesthesia. Most can return home the same day or after an overnight stay, depending on the surgeon's protocol and the complexity of the procedure.
Follow-up typically includes:
A postoperative appointment within 1–2 weeks
Incision site checks for healing and infection
Review of symptoms and activity restrictions
Instructions on when to resume work, driving, and light exercise
Pain is usually mild to moderate and can be managed with oral medications. Patients are encouraged to rest and avoid heavy lifting during the early phase of recovery.
Recovery Timeline and Activity Guidelines
Here’s what most patients can expect during the weeks following robotic tubal reversal:
Week 1: Rest at home, manage discomfort with pain relief, avoid bending or lifting
Week 2: Light walking and daily activities resume, most return to desk jobs
Weeks 3–4: Gradual return to normal routines and low-impact exercise
Week 5+: Full physical activity permitted unless otherwise directed
Incisions heal quickly, and most women find the recovery process to be shorter and less painful than anticipated.
When to Resume Trying for Pregnancy
While the physical recovery is fairly rapid, it’s important to allow the fallopian tubes sufficient time to heal before attempting conception. Most providers recommend waiting one full menstrual cycle—typically 4 to 6 weeks—before trying to become pregnant.
Your surgeon will confirm tubal healing during follow-up and may perform imaging or additional testing if necessary. In many cases, natural conception can be attempted shortly after recovery, with no need for further intervention.
Risks and Special Considerations
While robotic tubal reversal is considered safe and effective in the hands of an experienced surgeon, no surgical procedure is without risk. Patients should be aware of the potential complications and individual factors that may influence their outcomes. In some cases, alternative fertility treatments like IVF may offer better results depending on personal circumstances.
Potential Surgical Risks
Like any abdominal surgery performed under general anesthesia, robotic tubal reversal carries a small risk of complications. These risks are rare but important to understand:
Infection at the incision sites
Bleeding during or after surgery
Adverse reaction to anesthesia
Formation of internal scar tissue (adhesions)
Damage to nearby organs (bowel, bladder, blood vessels)
Persistent pelvic pain following surgery
Incomplete tubal patency or failed reconnection
Your surgeon will take precautions to minimize these risks and will explain any specific concerns based on your medical history.
Factors That Affect Success Rates
Not all patients have the same likelihood of success. Several biological and surgical variables can influence whether tubal reversal will lead to a natural pregnancy:
Age (women under 38 generally see higher success rates)
Method of original tubal ligation (clips and rings are easier to reverse than burned or removed segments)
Remaining length and quality of fallopian tubes
Presence of scar tissue from prior abdominal or pelvic surgeries
Overall reproductive health (ovarian reserve, partner fertility, hormonal status)
A comprehensive preoperative evaluation can help determine your individual chances of success.
Alternatives to Tubal Reversal (Including IVF)
For some women, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be a more effective or practical option. IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes entirely and may be preferred in cases where:
Tubes were extensively damaged or removed
Reversal surgery is not feasible due to health risks
Speed of conception is a top priority
Advanced maternal age reduces natural fertility odds
Discussing all available options with a fertility specialist ensures you choose the path best suited to your medical needs and family-building goals.
Conclusion
Robotic tubal reversal is a highly advanced and effective option for women who wish to restore their fertility after tubal ligation. By combining minimally invasive access with enhanced surgical precision, this technique offers the potential for natural conception with a shorter recovery time and fewer complications compared to traditional methods.
Understanding how the procedure works—from preparation to postoperative care—empowers patients to make informed decisions about their reproductive future. Factors like age, health history, and previous ligation technique all play a role in determining whether this approach is right for you.
Dr. Jason Neef is a board-certified surgeon with specialized expertise in robotic and laparoscopic tubal reversal. He works closely with each patient to determine the best surgical path based on individual goals and medical history.
If you're considering tubal reversal, consulting a qualified specialist like Dr. Neef can be the first step toward restoring your fertility and growing your family. Contact us.
Restore your fertility with advanced robotic tubal reversal today.
Call (817) 568-8731Categories:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Robotic tubal reversal is a minimally invasive surgery that uses robotic-assisted technology to reconnect the fallopian tubes after a previous tubal ligation. It enables natural conception by restoring the normal pathway for egg and sperm to meet.
-
Robotic reversal offers enhanced precision, 3D visualization, and wristed instruments that improve suturing accuracy. Traditional methods rely on manual laparoscopic or open techniques and may not offer the same level of fine control.
-
Most patients experience mild to moderate discomfort after surgery. Pain is typically well-managed with oral medications and resolves within a few days. Minimally invasive access also means fewer complications and faster healing.
-
Recovery time varies, but most patients resume light activity within 7 to 10 days and return to full function in about 3 to 4 weeks. Complete healing of the fallopian tubes may take slightly longer.
-
You can typically begin trying to conceive after your first menstrual cycle post-surgery, usually around 4 to 6 weeks. Your surgeon will confirm healing and readiness during a follow-up visit.
-
Success rates range from 60% to 80% depending on age, tube quality, and overall fertility health. Women under 38 with healthy tubes tend to have the highest success rates.
-
In most cases, no. Tubal reversal is considered an elective fertility procedure and is not covered by standard insurance plans. Patients usually pay out of pocket or through financing options.
-
While complications are rare, risks include infection, bleeding, anesthesia reactions, and internal adhesions. A qualified surgeon will take precautions to minimize these issues.
-
Not always. Procedures that involved burning or removing large sections of the fallopian tubes may not be reversible. Your surgeon will evaluate whether your anatomy supports successful repair.
-
Dr. Jason Neef is a board-certified surgeon experienced in both robotic and laparoscopic tubal reversal. He provides individualized care, transparent pricing, and a proven track record of helping patients restore their fertility through advanced surgical methods.