Total vs Partial Robotic Hysterectomy: Key Differenc
Categories:
By: Ethan Cole
Robotic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed with the assistance of advanced robotic technology. This cutting-edge technique allows surgeons to perform the operation through small incisions using robotic arms controlled with high precision, offering enhanced visualization and greater dexterity compared to traditional surgery. Because of these advantages, robotic hysterectomy often results in less blood loss, reduced pain, smaller scars, and faster recovery times.
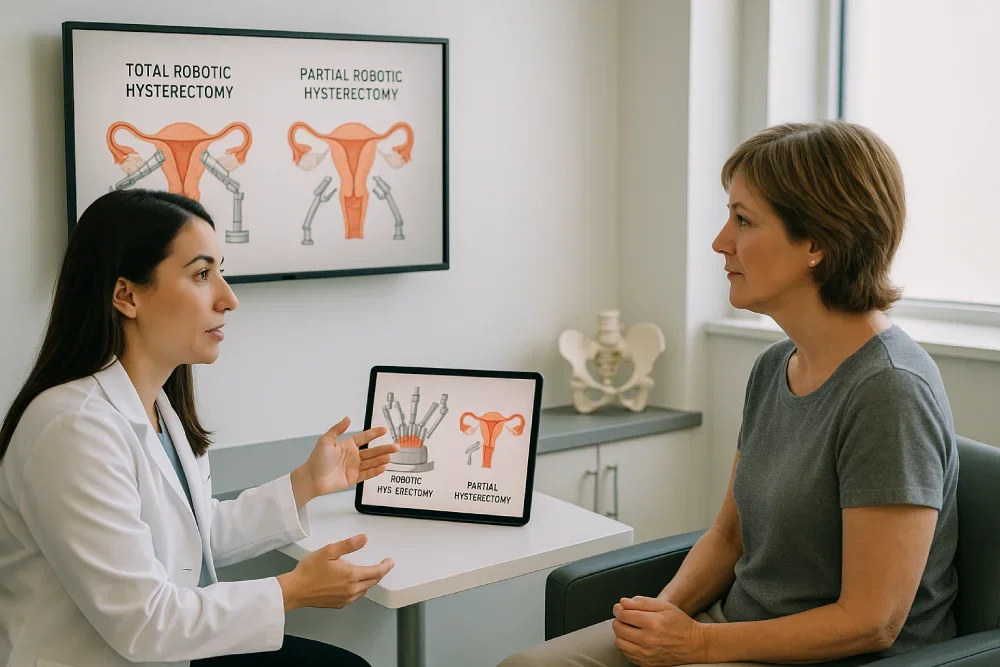
Understanding the difference between total and partial robotic hysterectomy is essential for anyone considering this surgery. Total robotic hysterectomy involves the removal of the entire uterus, including the cervix, while partial (or supracervical) robotic hysterectomy removes only the upper part of the uterus, preserving the cervix. Both options use robotic assistance but have distinct surgical goals, benefits, and post-operative considerations.
This guide explores the key differences between total and partial robotic hysterectomy to help patients make informed decisions alongside their healthcare provider.
Key Takeaways
Total robotic hysterectomy removes the uterus and cervix, while partial (supracervical) removes only the upper uterus, preserving the cervix for benign conditions.
Partial hysterectomy often allows faster recovery (3–4 weeks) compared to total (4–6 weeks), due to less surgical complexity and cervix preservation.
Total hysterectomy eliminates the need for cervical screening but may slightly impact sexual function, while partial requires ongoing Pap smears but may better preserve sexual sensation.
Both procedures use robotic precision to reduce blood loss, scarring, and pain, offering faster recovery than traditional open surgery.
Choice depends on medical indications—total is usually for cancer or severe disease, while partial is often chosen for benign conditions and patient preference.
Robotic surgery improves surgeon ergonomics, visualization, and precision, lowering complications in complex cases such as obesity, adhesions, or large uteri.
What is Total Robotic Hysterectomy?
Total robotic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves the complete removal of the uterus along with the cervix using advanced robotic technology. This technique allows surgeons to perform the operation with high precision through several small incisions in the abdomen. Equipped with 3D magnification and robotic arms, the surgeon controls the instruments remotely from a console, enabling precise movements that are often more refined than traditional laparoscopic methods.
This procedure is commonly recommended for medical conditions such as endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, uterine fibroids, or other severe uterine diseases requiring full removal of the uterus and cervix. The robotic approach offers multiple advantages including reduced blood loss, minimized surgical trauma, less post-operative pain, smaller scars, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
By preserving the advantages of minimally invasive surgery while enhancing surgical dexterity and visualization, total robotic hysterectomy provides patients with a safe and effective surgical option for addressing various gynecologic conditions.
What is Partial (Supracervical) Robotic Hysterectomy?
Partial robotic hysterectomy, also known as supracervical or subtotal hysterectomy, is a minimally invasive surgery that removes the upper part of the uterus but preserves the cervix.
It is often recommended for benign uterine conditions such as fibroids, abnormal bleeding, or non-cancerous growths when removing the cervix is not necessary.
The procedure uses robotic technology with small abdominal incisions, providing surgeons enhanced precision and visualization.
Patients typically experience less operative time, less blood loss, and quicker recovery compared to total hysterectomy.
Since the cervix remains, patients require regular cervical cancer screenings post-surgery.
Key Differences Between Total and Partial Robotic Hysterectomy
|
Feature |
Total Robotic Hysterectomy |
Partial (Supracervical) Robotic Hysterectomy |
|
Uterus Removal |
Entire uterus including cervix removed |
Upper uterus removed; cervix preserved |
|
Common Indications |
Cancer, severe uterine disease |
Benign conditions like fibroids |
|
Procedure Length |
Usually longer |
Usually shorter |
|
Recovery Time |
Longer recovery expected |
Faster recovery |
|
Cervical Cancer Screening Post-Surgery |
Not needed (cervix is removed) |
Required (cervix remains) |
|
Impact on Sexual Function |
May affect sexual function |
May better preserve sexual function |
Both procedures leverage robotic technology to enhance surgical precision, reduce blood loss, and shorten hospital stay compared to open surgery.
Advantages of Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy
Robotic-assisted hysterectomy offers several significant advantages over traditional open and laparoscopic hysterectomy techniques. These benefits stem from the precision and minimally invasive nature of robotic technology:
Smaller Incisions and Less Scarring: The surgery is performed through 3-5 small incisions (5-12mm), leading to minimal visible scarring compared to large abdominal incisions of traditional surgery.
Reduced Blood Loss: Blood loss during robotic hysterectomy is typically less than 100mL, lowering the need for transfusions and reducing surgical risks.
Less Postoperative Pain: Smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma result in less pain and decreased reliance on opioid pain medications after surgery.
Shorter Hospital Stay: Most patients spend significantly less time in the hospital—often just hours—compared to several days for open surgery.
Faster Recovery: Patients generally recover in 3-4 weeks rather than 6-8 weeks, allowing a quicker return to daily activities and work.
Improved Surgical Precision: The robotic system provides surgeons with enhanced visualization (3D, magnified view) and instrument dexterity that exceeds the human wrist’s range of motion. This precision reduces the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Lower Risk of Complications: Research shows fewer wound infections, reduced post-operative adhesion formation, and better outcomes in complex cases such as obesity or extensive pelvic adhesions.
Better Cancer Outcomes: For early-stage uterine cancer, robotic hysterectomy has demonstrated improved survival rates compared to open surgery.
Enhanced Surgeon Ergonomics: The robotic console reduces surgeon fatigue during long procedures, potentially improving overall surgical quality.
In sum, robotic-assisted hysterectomy combines the advantages of minimally invasive surgery with state-of-the-art robotic technology, leading to safer procedures, quicker healing, and improved patient satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Procedure: Factors to Consider
Choosing between total and partial robotic hysterectomy depends on multiple factors including medical condition, patient preferences, and surgeon recommendations. Below is a comprehensive table summarizing key considerations for selecting the most appropriate robotic hysterectomy procedure:
|
Factor |
Total Robotic Hysterectomy |
Partial (Supracervical) Robotic Hysterectomy |
|
Medical Indications |
Conditions requiring full uterine and cervical removal such as uterine or cervical cancer, severe uterine disease |
Benign conditions like fibroids, abnormal bleeding, where cervix preservation is safe |
|
Risk of Cervical Cancer |
Eliminated by cervix removal |
Cervix remains, so continued cervical screening needed |
|
Surgical Risk |
Slightly higher due to more extensive surgery |
Lower surgical risk and complications |
|
Recovery Time |
Typically longer recovery (up to 6 weeks) |
Generally shorter recovery (3-4 weeks) |
|
Impact on Sexual Function |
Possible impact due to cervix removal |
Potentially better preservation of sexual function |
|
Future Health Monitoring |
No cervical cancer screening required |
Regular Pap smears and HPV testing are necessary |
|
Surgeon Recommendation |
Preferred for cancer or extensive uterine disease |
Suitable for benign disease and patient preference |
|
Patient Preference |
May prefer full removal for peace of mind |
May prefer cervix preservation for better function |
|
Complexity of Surgery |
More complex, requires experienced surgeon |
Less complex, may be quicker |
Additional Considerations
Age and reproductive goals: Both procedures are for women who do not plan to conceive post-surgery.
Surgeon experience and hospital facilities: Availability of experienced robotic surgeons may influence procedure choice.
Overall health status: Patient comorbidities can impact surgical suitability and recovery.
Making an informed choice requires discussing these factors with a gynecologic surgeon to evaluate which robotic hysterectomy approach aligns best with individual needs and medical conditions.
Recovery and Aftercare for Both Procedures
Recovery from both total and partial robotic hysterectomy tends to be significantly faster and less painful than traditional open hysterectomy due to the minimally invasive nature of robotic-assisted surgery.
Typical Recovery Timeline
|
Recovery Stage |
What to Expect |
Activity Recommendations |
|
Week 1 |
Hospital discharge (often same or next day); manage mild pain or gas discomfort; rest and gentle walking |
Avoid heavy lifting (>10-15 lbs); short, gentle walks encouraged |
|
Weeks 2-3 |
Energy increases; pain subsides; can resume desk work and driving |
Continue light activity; avoid strenuous exercise or heavy lifting |
|
Weeks 4-6 |
Internal healing continues (especially vaginal cuff in total hysterectomy); pelvic rest recommended |
Avoid intercourse and vaginal penetration until cleared by doctor; gradual return to normal activity |
|
Full Recovery by 6-8 Weeks |
Most patients returned to full normal activities including exercise and sexual activity |
Follow surgeon clearance; ease into strenuous activities gradually |
Key Recovery Considerations
Pain Management: Post-operative pain is usually mild and managed with prescribed or over-the-counter medications.
Hospital Stay: Most patients leave the hospital the same day or after an overnight stay.
Activity Restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for about 6 weeks. Walking is encouraged to improve circulation and healing.
Vaginal Discharge: Some bloody or watery discharge is normal for several weeks after surgery.
Follow-Up: A 6-week post-operative appointment is important to assess healing, especially vaginal cuff healing in total hysterectomy patients.
Sexual Activity: Should generally be avoided for 4-6 weeks until healing is confirmed.
Emotional Well-being: It is normal to have mixed emotions; support from healthcare providers can help in coping.
Differences in Aftercare for Total vs Partial
|
Aspect |
Total Robotic Hysterectomy |
Partial Robotic Hysterectomy |
|
Vaginal Cuff Healing |
Requires special attention; no cervix remains |
Cervix remains, so no vaginal cuff healing needed |
|
Cervical Cancer Screening |
Not needed post-surgery |
Continued regular cervical screening |
|
Possible Light Bleeding |
Vaginal bleeding typically stops after weeks |
Some light bleeding may persist up to a year due to retained cervix |
|
Sexual Function Recovery |
May experience changes due to cervix removal |
Potentially quicker and less impact |
Most patients find robotic hysterectomy offers faster physical recovery with less pain and quicker return to regular life compared to traditional surgery.
Conclusion
Robotic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgery where surgeons remove the uterus using robotic arms controlled with precision. It offers shorter recovery times, smaller incisions, and less scarring compared to traditional methods.
Total robotic hysterectomy removes the entire uterus and cervix, typically for cancer or severe disease, while partial robotic hysterectomy removes only the upper uterus, preserving the cervix for benign conditions.
Both procedures provide faster healing and less pain, but differ in recovery and post-surgery care. Patients should consult their doctors to choose the best option based on their condition.
Explore your robotic hysterectomy options with Dr. Jason Neef and get personalized guidance on whether total or partial is right for you. Schedule your consultation today to make an informed decision for your health and recovery.
Explore robotic hysterectomy options with Dr. Neef today.
Call (817) 568-8731Categories:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Robotic partial hysterectomy typically has a slightly faster recovery (3-4 weeks) compared to total hysterectomy (4-6 weeks), due to less extensive surgery and cervix preservation. Both are faster than traditional open surgery recovery times.
-
Total robotic hysterectomy carries slightly higher risks like vaginal cuff complications, while partial retains cervix with ongoing cervical cancer screening risk; partial has lower surgical complexity and fewer immediate post-op risks.
-
Robotic total hysterectomy usually takes 30-40 minutes longer than laparoscopic due to set-up and docking time, though it offers improved surgical precision and dexterity especially in complex cases.
-
Partial robotic hysterectomy is preferred when cervix preservation benefits function and screening, for benign fibroids or bleeding without cervical pathology, reducing recovery time and surgical risks.
-
Cervix preservation requires continued cervical cancer screening but may help maintain sexual sensation and pelvic support, possibly improving sexual function compared to total removal.
-
Most robotic hysterectomy patients are discharged within 24 hours; some centers discharge within 6 hours post-op, enabling faster return to home recovery.
-
Decision depends on medical diagnosis, cancer risk, patient preference, surgeon experience, and anticipated impact on function and screening needs.
-
Robotic hysterectomy significantly reduces blood loss compared to open surgery, usually less than 100mL, minimizing transfusion needs.
-
Patients avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activity, and vaginal intercourse for 4-6 weeks, with gradual return to normal activities as healing progresses.
-
Robotic console reduces surgeon fatigue with enhanced wrist articulation and 3D visualization, improving precision, especially in complex or obese patients.